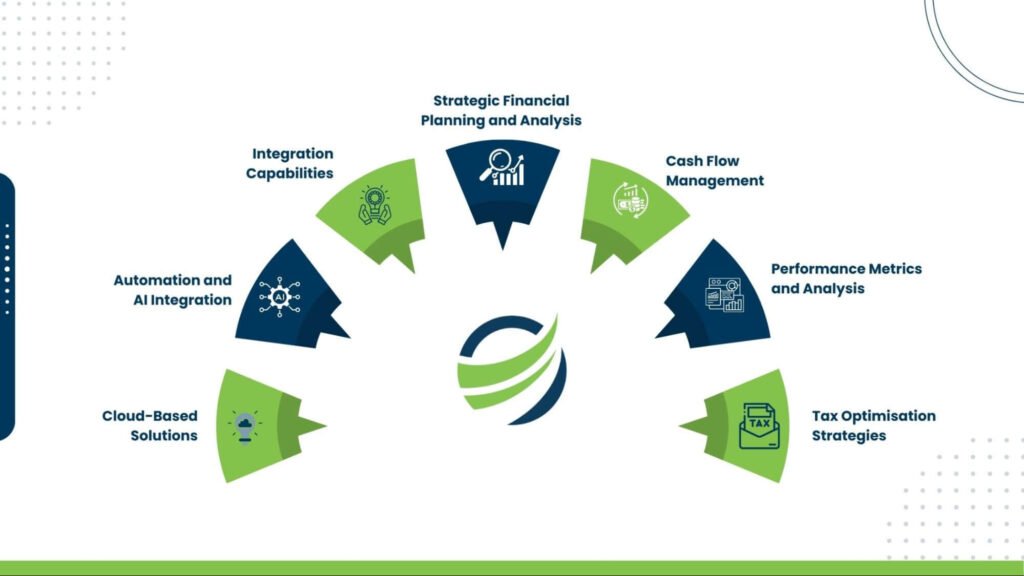
Canada’s financial landscape operates under a sophisticated framework of accounting standards designed to ensure transparency, consistency, and reliability in financial reporting.
Generally accepted accounting principles in Canada serve as the cornerstone of financial accountability for businesses across the nation, providing CPAs and accountants with the essential guidelines needed to maintain professional standards and regulatory compliance.
Key Takeaways
- Canada operates a multi-framework accounting model with IFRS for public companies and ASPE for private enterprises
- Over 220,000 CPAs across Canada currently apply Canadian GAAP principles in their professional practice
- IFRS has been mandatory for publicly accountable enterprises since January 2011
- Private companies can choose between IFRS and ASPE based on their specific business needs
- Canadian GAAP compliance is overseen by the Accounting Standards Board (AcSB) under CPA Canada
The Evolution of Canadian GAAP
The framework of Canadian GAAP has undergone significant transformation over the past decade. Historically managed by the Canadian Institute of Chartered Accountants (CICA), Canada made a strategic decision in 2011 to align with global accounting practices by adopting International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
According to recent industry statistics, approximately 75% of companies have reported increased efficiency since adopting these modern accounting frameworks, with 78% experiencing notable cost savings through improved standardisation.
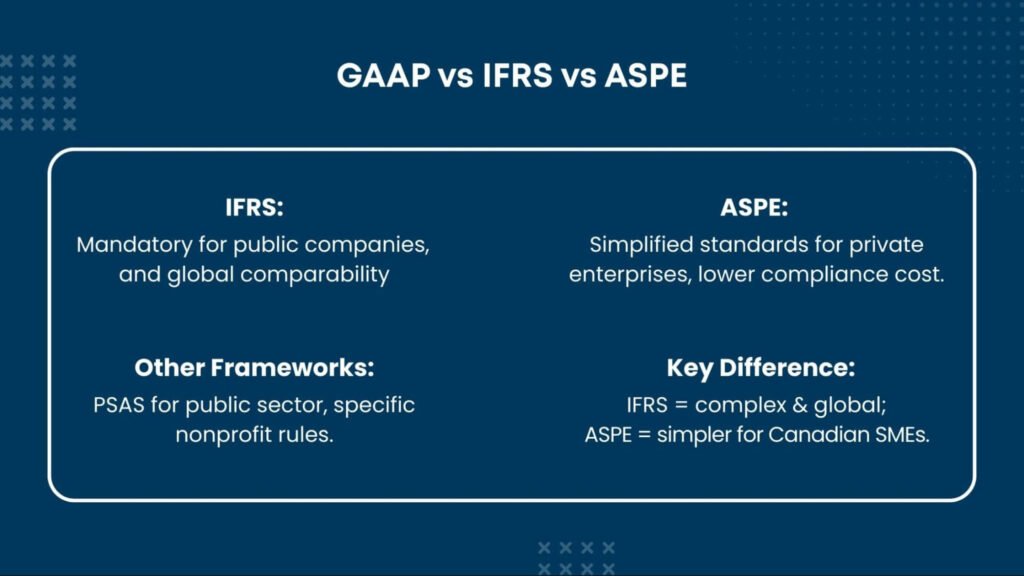
Understanding the Multi-Framework Model
Canadian general accounting principles now operate under what experts call a multi-framework model This sophisticated approach recognises that different types of organisations have varying reporting needs and stakeholder requirements.

IFRS for Public Companies
International Financial Reporting Standards form Part I of the CPA Canada Handbook and apply to publicly accountable enterprises. These companies must comply with IFRS because they either:
- Issue debt or equity instruments traded in public markets
- Hold assets in a fiduciary capacity for broad groups of outsiders
- They are regulated entities with significant public interest
The adoption of IFRS has positioned Canadian businesses favorably in global markets. Research indicates that companies using IFRS report median compensation growth of 7.7% for their financial professionals, outpacing Canada’s 6.4% inflation rate.
ASPE for Private Enterprises
GAAP principles in Canada also include Accounting Standards for Private Enterprises (ASPE), which provides a simplified framework specifically designed for private companies. ASPE offers several advantages:
- Reduced compliance costs compared to IFRS
- Less complex disclosure requirements
- Focus on historical cost rather than fair value measurements
- Greater flexibility in accounting policy choices
Industry data shows that 74.6% of Canadian accounting establishments employ fewer than five professionals, making ASPE particularly relevant for smaller firms seeking cost-effective compliance solutions.
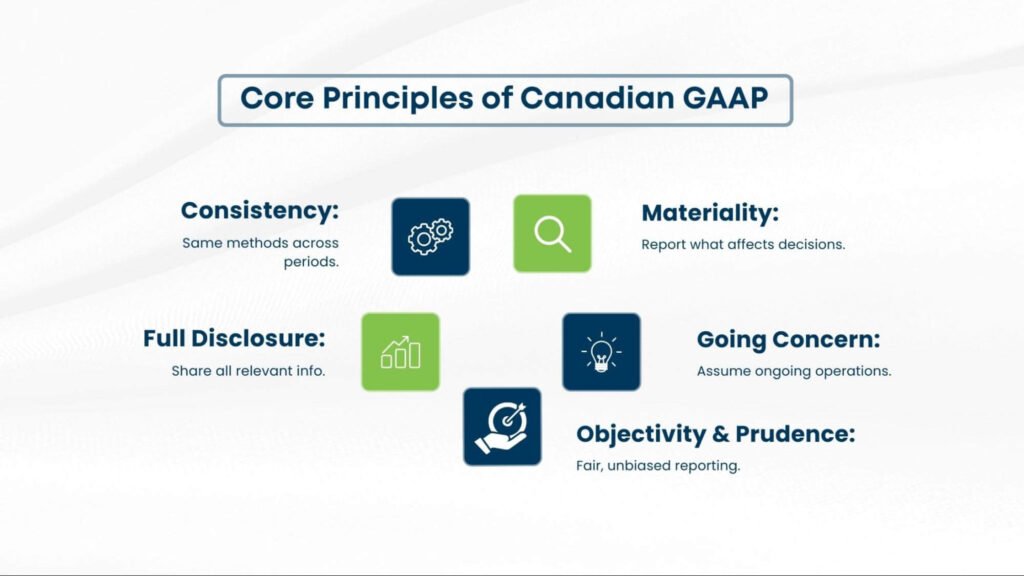
Core Principles Governing Canadian Financial Reporting
The foundation of generally accepted accounting principles in Canada rests on several fundamental concepts that ensure consistency across all frameworks:
Revenue Recognition
Under Canadian standards, revenue must be recognised when earned and measurable, regardless of when payment is received. This principle ensures accurate representation of a company’s financial performance.
Matching Principle
Expenses are recorded in the same period as the revenues they help generate, providing stakeholders with a clear picture of profitability and operational efficiency.
Full Disclosure
Companies must disclose all material information that could influence decision-making by financial statement users, promoting transparency and informed decision-making.
Cost Principle
Assets are typically recorded at their historical cost, providing a reliable and objective basis for financial reporting that enhances comparability across periods.
Regulatory Oversight and Compliance
The Canadian accounting principles framework operates under the oversight of the Accounting Standards Board (AcSB), which works in conjunction with international standard-setters to ensure Canadian standards remain globally competitive while meeting domestic needs.
Recent compensation studies reveal that Canadian CPAs earn a median salary of $154,000, reflecting the high demand for professionals skilled in these complex regulatory requirements. This represents a 47% increase over the past 12 years, demonstrating the growing importance of GAAP expertise in the Canadian marketplace.
Industry Impact and Statistics
The implementation of modern GAAP accounting principles has yielded measurable benefits across Canadian industries:
- 82% of companies report improved regulatory compliance since adopting current frameworks
- The Oil & Gas sector leads compensation at $200,000 median for GAAP-compliant professionals
- Alberta shows the highest provincial compensation at $169,000 median for CPAs
- The software industry demonstrates notable growth with $178,000 median compensation
Technology Integration and Future Developments
Modern Canadian GAAP implementation increasingly relies on sophisticated software solutions and cloud-based platforms. Leading accounting firms now utilise advanced technologies to ensure compliance while reducing operational costs.
The profession continues evolving with emerging technologies, as evidenced by 33% of software sector professionals reporting annual pay increases exceeding 10%. This growth reflects the increasing integration of technology in GAAP compliance and financial reporting processes.
Strategic Considerations for Canadian Businesses
Organisations must carefully evaluate their choice between IFRS and ASPE based on several factors:
Choose IFRS when:
- Seeking international investment or expansion
- Planning public offerings or listings
- Operating in regulated industries
- Requiring global financial statement comparability
Consider ASPE when:
- Operating as a private enterprise
- Prioritising cost-effective compliance
- Working with domestic stakeholders primarily
- Seeking simplified reporting requirements
Professional Development and Career Opportunities
The demand for GAAP-proficient professionals remains robust across Canada. Current statistics show a 3.6% unemployment rate for finance and accounting professionals, indicating strong job security for those with relevant expertise.
OUTSOURCING ACCOUNTING SOLUTIONS have become increasingly popular, with many firms partnering with specialists to ensure compliance while focusing on core business operations. This trend has created new opportunities for both domestic and international collaboration in financial reporting.
For organisations seeking expert guidance, partnering with experienced FINANCIAL REPORTING SPECIALISTS can provide access to cutting-edge knowledge and technology while ensuring full compliance with Canadian standards.
Implementation Best Practices
Successful GAAP implementation requires careful planning and execution. Best practices include:
- Regular training for accounting staff on current standards
- Investment in appropriate accounting software and systems
- Establishment of robust internal controls and review processes
- Engagement with qualified professionals for complex transactions
Many organisations find value in Professional accounting services that provide ongoing support and expertise throughout the implementation process.
Looking Forward
As Canadian businesses continue to evolve in an increasingly complex global marketplace, understanding and properly implementing generally accepted accounting principles remains crucial for success. The multi-framework approach adopted by Canada provides flexibility while maintaining the high standards expected by stakeholders.
For businesses navigating these complex requirements, working with experienced professionals who understand both the technical aspects of GAAP and the practical challenges of implementation can provide significant competitive advantages in today’s demanding business environment.